Mol Autism. 2023 Jan 5;14(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13229-022-00532-3.
Immune activation during pregnancy exacerbates ASD-related alterations in Shank3-deficient mice (妊娠中の免疫活性化がShank3欠損マウスのASD関連症状を悪化させる)
Ekaterina Atanasova 1, Andrea Pérez Arévalo 1, Ines Graf 1, Rong Zhang 2, Juergen Bockmann 1, Anne-Kathrin Lutz # 3, Tobias M Boeckers # 4 5
Affiliations
1Institute for Anatomy and Cell Biology, Ulm University, Ulm, Germany.
2Neuroscience Research Institute, Health Science Centre, Peking University, Peking, China.
3Institute for Anatomy and Cell Biology, Ulm University, Ulm, Germany. Anne-Kathrin.Lutz@uni-ulm.de.
4Institute for Anatomy and Cell Biology, Ulm University, Ulm, Germany. Tobias.Boeckers@uni-ulm.de.
5Deutsches Zentrum für Neurodegenerative Erkrankungen (DZNE), Ulm Site, Ulm, Germany. Tobias.Boeckers@uni-ulm.de. #Contributed equally.
DZNE-Standort Ulmは、ドイツのアルム市にあるドイツ脳研究所 (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases: DZNE) の研究施設のことです。この施設は、神経変性疾患の研究、診断、治療などに関連する多角的なアプローチを通じて、これらの疾患の治療法の開発、予防、および対策に焦点を当てています。(ChatGPTの回答)

Abstract
Background
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is mainly characterized by deficits in social interaction and communication and repetitive behaviors. Known causes of ASD are mutations of certain risk genes like the postsynaptic protein SHANK3 and environmental factors including prenatal infections.
Methods
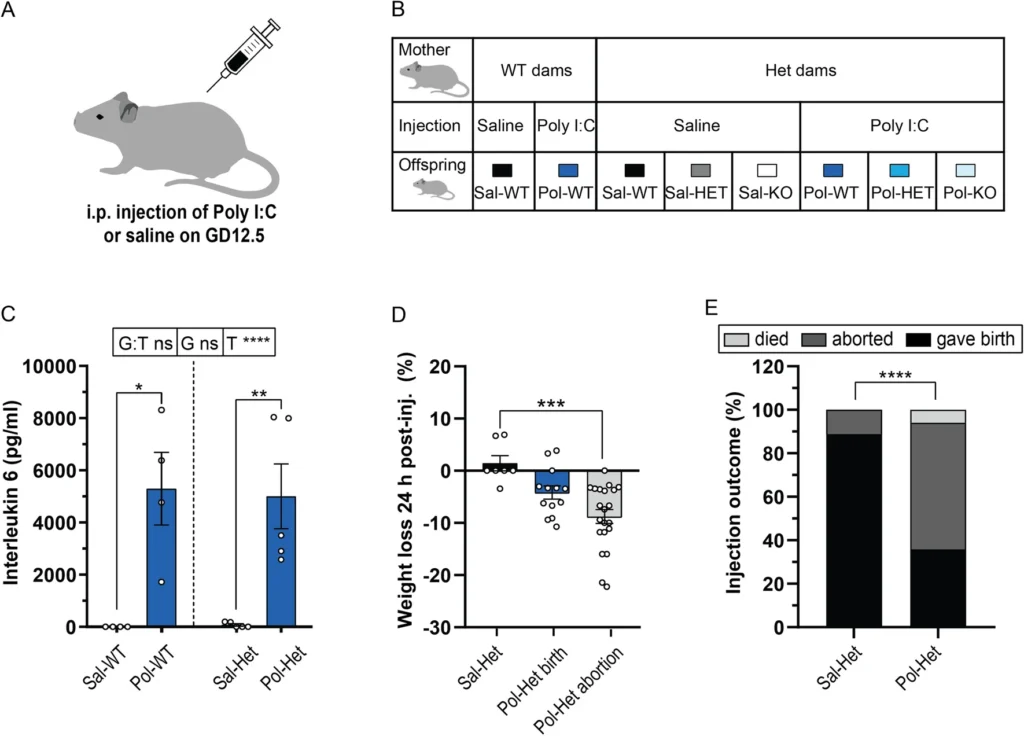
To analyze the gene-environment interplay in ASD, we combined the Shank3Δ11−/− ASD mouse model with maternal immune activation (MIA) via an intraperitoneal injection of polyinosinic/polycytidylic acid (Poly I:C) on gestational day 12.5. The offspring of the injected dams was further analyzed for autistic-like behaviors and comorbidities followed by biochemical experiments with a focus on synaptic analysis.
Results
We show that the two-hit mice exhibit excessive grooming and deficits in social behavior more prominently than the Shank3Δ11−/− mice. Interestingly, these behavioral changes were accompanied by an unexpected upregulation of postsynaptic density (PSD) proteins at excitatory synapses in striatum, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
Limitations
We found several PSD proteins to be increased in the two-hit mice; however, we can only speculate about possible pathways behind the worsening of the autistic phenotype in those mice.
Conclusions
With this study, we demonstrate that there is an interplay between genetic susceptibility and environmental factors defining the severity of ASD symptoms. Moreover, we show that a general misbalance of PSD proteins at excitatory synapses is linked to ASD symptoms, making this two-hit model a promising tool for the investigation of the complex pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders.
〇背景
自閉スペクトラム症(ASD)は、社会的相互作用やコミュニケーションの障害、反復的な行動などを主な特徴とする。ASDの原因として、シナプス後タンパク質SHANK3のような特定のリスク遺伝子の変異や、出生前の感染を含む環境因子が知られている。
〇研究方法
ASDにおける遺伝子と環境の相互作用を解析するために、Shank3Δ11-/-ASDモデルマウスに妊娠12.5日目にPoly (I:C)を腹腔内投与して母体免疫活性化(MIA)を併用することとした。さらにその子孫について、自閉症様の行動や併存疾患を分析し、シナプス解析を中心とした生化学的実験を行った。
〇研究成果
2ヒットマウスは、Shank3Δ11-/-マウスよりも顕著に過剰なグルーミングと社会的行動の障害を示すことを示す。興味深いことに、これらの行動の変化には、線条体、海馬、前頭前野の興奮性シナプスにおけるシナプス後密度(PSD)タンパク質の予想外の上昇を伴っていた。
〇本研究の限界
2ヒットマウスでは、いくつかのPSDタンパク質が増加していた。しかし、これらのマウスで自閉症表現型が悪化する経路については、推測することしかできない。
〇結論
本研究により、ASDの重症度を規定する遺伝的感受性と環境要因の間に相互作用があることが示された。さらに、興奮性シナプスにおけるPSDタンパク質の一般的な不均衡がASD症状に関連することを示し、この2ヒットモデルが神経発達障害の複雑な病態生理を研究するための有望なツールであることを示した。
結論
生理食塩水を投与したマウスの子孫である雄のShank3Δ11-/-マウスは、自閉症の中核症状、すなわち社会的アプローチとコミュニケーションの障害、セルフグルーミングの増加を示し、同時に分析したすべての領域でいくつかのシナプス後タンパク質の発現が減少し、組織全体よりもPSD(シナプス後密度)においてより顕著に発現が見られた。Poly (I:C)注射に対する母親の免疫反応は、血清中のInterleukin- 6の増加や病気行動など深刻であったにもかかわらず、それらのdamの野生型雄の子供は、軽度の自閉症様表現型と海馬のみにおけるシナプス後タンパク質の発現の減少を示しただけであった。最後に、母方のPoly (I:C)処理は、2ヒットマウスには異なる影響を与えるようであった。彼らは、生理食塩水-KOマウスと比較して、PSDのいくつかのタンパク質のレベルが増加する一方で、自閉症の中核症状のみが悪化することを示した。自閉症様の表現型が増悪するメカニズムを理解するためには、2ヒットマウスの生化学的変化の特徴をさらに明らかにする必要があるが、このモデルはASDの文脈における遺伝的感受性と環境要因の相互作用を調べるための有望なツールであると思われる。また、環境因子は操作の難易度が低いため、治療法の開発がより容易になることを意味している。今後、このモデルで自閉症の病態に関わる経路が解明されれば、ASD患者に対する治療法の可能性が広がる
