Cell Reports
Volume 40, Issue 11, 13 September 2022, 111324
Article
Restoration of mitochondria axonal transport by adaptor Disc1 supplementation prevents neurodegeneration and rescues visual function (アダプターDisc1の補充によるミトコンドリア軸索輸送の回復が神経変性を防ぎ、視覚機能を回復させる)
Heberto Quintero, Yukihiro Shiga, Nicolas Belforte, Luis Alarcon-Martinez, Sana El Hajji, Deborah Villafranca-Baughman, FlorenceDotigny, AdrianaDi Polo
1. Department of Neuroscience, University of Montreal, PO Box 6128, Station Centre-ville, Montreal, QC H3C 3J7, Canada
2. Neuroscience Division, Centre de recherche du Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CRCHUM), 900 Saint Denis Street, Montreal, QC H2X 0A9, Canada
モントリオール大学は、ケベック州・モントリオール市に本部を置くカナダの国立大学である。学生数は約66,000人。フランス語の大学としてはフランスのパリ大学についで世界で2番目の規模であると同時に、カナダ全土の総合大学としても上位トップ5に入る名門校である。(wikipedia)
Received 4 April 2022, Revised 1 July 2022, Accepted 17 August 2022, Available online 13 September 2022, Version of Record 13 September 2022.
Published: September 13, 2022
Highlights
•Anterograde axonal transport of mitochondria is compromised in vulnerable retinal neurons
•Ocular hypertensive stress impairs Disc1 expression and mitochondrial movement
•Disc1 supplementation restores mitochondrial transport and promotes neuronal survival
•Recovery of light-evoked responses and visual behavior is achieved by Disc1 gene therapy
Keywords: mitochondria axonal transportmetabolic stressneuronal ATP productionglaucomadisrupted in schizophrenia 1retinal ganglion cellneuroprotectionvision restoration
Research topic(s)
CP: Neuroscience
Summary
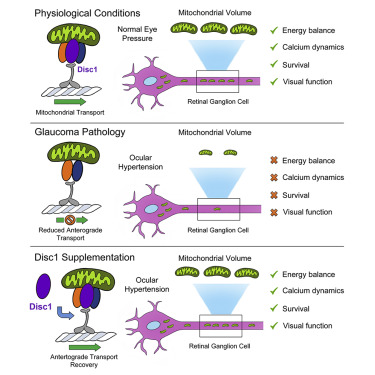
Deficits in mitochondrial transport are a common feature of neurodegenerative diseases. We investigated whether loss of components of the mitochondrial transport machinery impinge directly on metabolic stress, neuronal death, and circuit dysfunction. Using multiphoton microscope live imaging, we showed that ocular hypertension, a major risk factor in glaucoma, disrupts mitochondria anterograde axonal transport leading to energy decline in vulnerable neurons. Gene- and protein-expression analysis revealed loss of the adaptor disrupted in schizophrenia 1 (Disc1) in retinal neurons subjected to high intraocular pressure. Disc1 gene delivery was sufficient to rescue anterograde transport and replenish axonal mitochondria. A genetically encoded ATP sensor combined with longitudinal live imaging showed that Disc1 supplementation increased ATP production in stressed neurons. Disc1 gene therapy promotes neuronal survival, reverses abnormal single-cell calcium dynamics, and restores visual responses. Our study demonstrates that enhancing anterograde mitochondrial transport is an effective strategy to alleviate metabolic stress and neurodegeneration.
概要
ミトコンドリア輸送の障害は、神経変性疾患の共通の特徴である。我々は、ミトコンドリア輸送装置の構成要素の喪失が、代謝ストレス、神経細胞死、回路機能障害に直接影響を与えるかどうかを調べた。多光子顕微鏡によるライブイメージングにより、緑内障の主要な危険因子である眼圧が、ミトコンドリアの順行性輸送(anterograde transport) を阻害し、障害を受けたニューロンのエネルギー減少につながることを明らかにした。遺伝子およびタンパク質発現解析の結果、高眼圧にさらされた網膜神経細胞では、disrupted in schizophrenia 1(Disc1)というアダプターが失われていることが判明した。Disc1の遺伝子導入により、anterograde transportが回復し、軸索のミトコンドリアが補充された。Genetically encoded ATP sensorと縦断的ライブイメージングを組み合わせることで、Disc1の補充がストレス下のニューロンにおけるATP産生を増加させることが示された。Disc1遺伝子治療は、ニューロンの生存を促進し、1細胞のカルシウム動態の異常を回復させ、視覚反応を回復させた。本研究は、順行性のミトコンドリア輸送を強化することが、代謝ストレスと神経変性を緩和する有効な戦略であることを実証している。
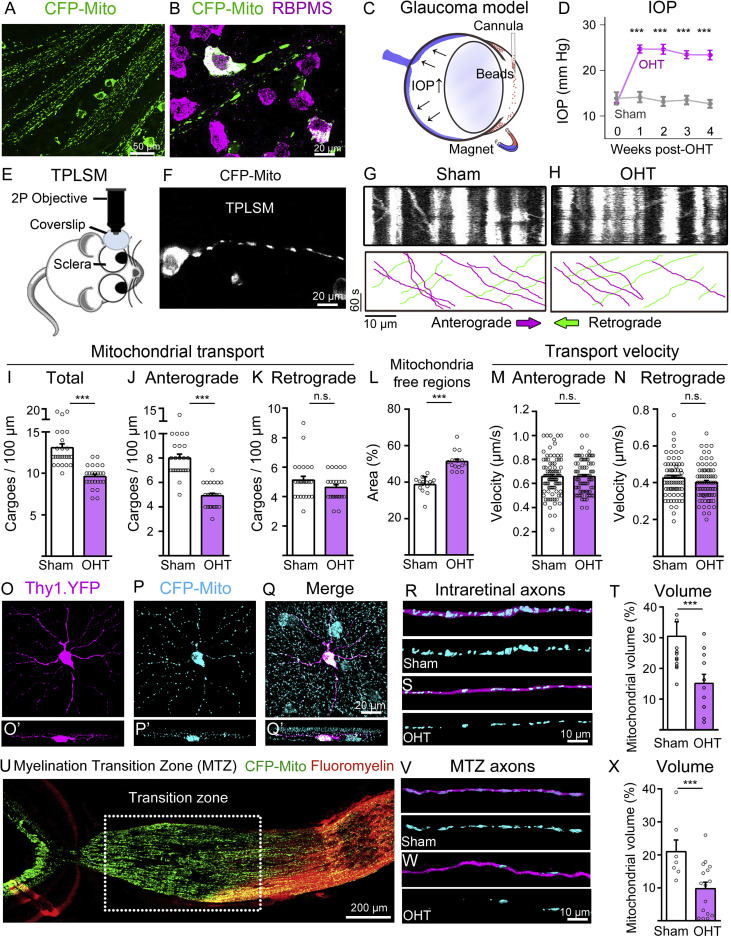
(A and B) Representative images of flat-mounted retinas from Thy1-CFP-MitoS mice show CFP-positive mitochondria in the soma and axons of RGCs, visualized with the cell-specific marker RBPMS.
(C and D) Schematic of the mouse glaucoma model induced by intracameral injection of magnetic microbeads, which block aqueous humour outflow leading to increased intraocular pressure (IOP) (N = 16 mice/group, two-way ANOVA with Šidák’s post hoc test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
(E and F) Setup for two-photon laser scanning microscopy (TPLSM) used for live imaging of mitochondria in individual RGC axons from Thy1-CFP-MitoS mice.
(G and H) Representative kymographs of TPLSM-recorded mitochondrial movement show anterograde (magenta) and retrograde (green) transport in sham and ocular hypertensive (OHT) eyes.
(I–K) Quantification of mitochondrial transport reveals marked reduction of total mitochondria mobility in glaucoma, with anterograde transport primarily affected while retrograde movement remained unchanged (sham: N = 14 mice, n = 25 axons; OHT: N = 14 mice, n = 25 axons, two-tailed Student’s t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, n.s., not significant).
(L) Increased mitochondria-free regions in axons from retinas subjected to OHT relative to sham retinas (sham: N = 8 mice, n = 15 axons; OHT: N = 8 mice, n = 15 axons, two-tailed Student’s t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
(M and N) The velocity of anterograde and retrograde transport is not affected in glaucoma (sham: N = 14 mice, n = 80 events; OHT: N = 14 mice, n = 80 events, two-tailed Student’s t test, n.s., not significant).
(O–Q) Representative images from Thy1-YFP-CFP-MitoS retinas show CFP-tagged mitochondria in YFP-labeled RGC compartments and (O′–Q′) their z stack projections.
(R–T) 3D reconstruction of individual intraretinal YFP axons show decreased mitochondrial volume in OHT compared with sham controls (sham: N = 4 mice, n = 12 axons; OHT: N = 4 mice, n = 12 axons, two-tailed Student’s t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
(U) Visualization of the optic nerve myelination transition zone (MTZ) in Thy1-YFP-CFP-MitoS mice using fluoromyelin.
(V–X) 3D reconstruction of individual MTZ-axons show loss of mitochondrial volume in glaucoma (sham: N = 4 mice, n = 10 axons; OHT: N = 8 mice, n = 16 axons; two-tailed Student’s t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. Scale bars: 200 (U), 50 (A), 20 (B, F, Q), and 10 μm (G, H, R–T, W).
本日は、ジャーナルクラブの後に学生がプログレスセミナーを行いました。
b9bebcb495f28be4ca73817c5ec7ea79


