Cell Reports Medicine Volume3,Issue4,100597,April 19,2022
Article
Autoantibodies against NCAM1 from patients with schizophrenia cause schizophrenia-related behavior and changes in synapses in mice (統合失調症患者由来のNCAM1に対する自己抗体がマウスにおいて統合失調症関連行動とシナプスの変化を引き起こす)
Hiroki Shiwaku,1,* Shingo Katayama,1 Kanoh Kondo,2 Yuri Nakano,1 Hikari Tanaka,2 Yuki Yoshioka,2 Kyota Fujita,2 Haruna Tamaki,3 Hironao Takebayashi,4 Omi Terasaki,4 Yukihiro Nagase,5 Teruyoshi Nagase,5 Tetsuo Kubota,6 Kinya Ishikawa,7 Hitoshi Okazawa,2 and Hidehiko Takahashi1*
1Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Tokyo Medical and Dental University Graduate School, Tokyo 113-8510, Japan
2Department of Neuropathology, Medical Research Institute and Center for Brain Integration Research, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo 113-8510, Japan 3Department of Neurology and Neurological Science, Tokyo Medical and Dental University Graduate School, Tokyo 113-8510, Japan
4Kurita Hospital, Kanagawa 212-0054, Japan
5Takatsuki Hospital, Tokyo 192-0005, Japan
6Department of Medical Technology, Tsukuba International University, Ibaraki 300-0051, Japan
7The Center for Personalized Medicine for Healthy Aging, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo 113-8510, Japan
塩飽ら(東京医科歯科大学精神行動医化学分野)は、統合失調症患者由来の抗NCAM1自己抗体をマウスに注射すると統合失調症関連行動を引き起こし、スパインやシナプスを変化させることを示した。
この自己抗体は統合失調症の症状の原因と考えられ、よって抗NCAM1自己抗体陽性の患者において治療の標的になり得ると考えられる。
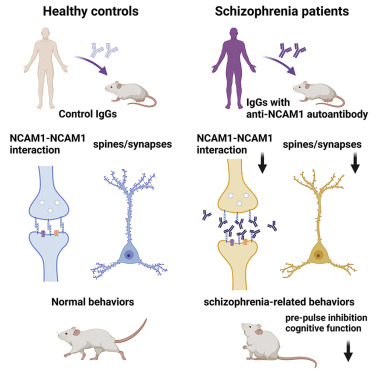
Hilights
・Some patients with schizophrenia are positive for anti NCAM1 autoantibodies
(統合失調症の患者の中には抗NCAM1自己抗体陽性の者がいる)
・ Anti-NCAM1 antibody from schizophrenia patients inhibits NCAM1-NCAM1 interactions
(統合失調症患者由来の抗NCAM1自己抗体はNCAM1-NCAM1相互作用を阻害する)
・Anti-NCAM1 antibody from schizophrenia patients reduces spines and synapses in mice
(統合失調症患者由来の抗NCAM1自己抗体はマウスのスパインとシナプスを減少させる)
・ Anti-NCAM1 antibody from patients induces schizophrenia‐related behavior
(患者由来の抗NCAM1自己抗体はマウスの統合失調症関連行動を誘発する)
Summary
From genetic and etiological studies, autoimmune mechanisms underlying schizophrenia are suspected; however, the details remain unclear. In this study, we describe autoantibodies against neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM1) in patients with schizophrenia (5.4%, cell-based assay; 6.7%, ELISA) in a Japanese cohort (n = 223). Anti-NCAM1 autoantibody disrupts both NCAM1-NCAM1 and NCAM1-glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) interactions. Furthermore, the anti-NCAM1 antibody purified from patients with schizophrenia interrupts NCAM1-Fyn interaction and inhibits phosphorylation of FAK, MEK1, and ERK1 when introduced into the cerebrospinal fluid of mice and also reduces the number of spines and synapses in frontal cortex. In addition, it induces schizophrenia-related behavior in mice, including deficient pre-pulse inhibition and cognitive impairment. In conclusion, anti-NCAM1 autoantibodies in patients with schizophrenia cause schizophrenia-related behavior and changes in synapses in mice. These antibodies may be a potential therapeutic target and serve as a biomarker to distinguish a small but treatable subgroup in heterogeneous patients with schizophrenia.
遺伝学的、病因学的な研究から、自己免疫機構が統合失調症に関わっている事が示唆されているが、詳細については未だ未解明である。
本研究では、日本人の統合失調症患者集団(n=223)由来の神経細胞接着分子(NCAM1)に対する自己抗体(cell-based assayで5.4%、ELISAで6.7%の患者に見られた)について述べる。
抗NCAM1自己抗体はNCAM1-NCAM1相互作用とNCAM1-グリア細胞由来神経栄養因子(GDNF)相互作用の両方を阻害する。
また、統合失調症患者から精製された抗NCAM1自己抗体は、マウスの脳脊髄液に注射するとNCAM1-Fyn相互作用を遮り、FAK、MEK1、ERK1のリン酸化を阻害して、前頭皮質のスパインとシナプスの数を減少させ、更にプレパルス抑制の低下や認知機能の障害を含むマウスの統合失調症関連行動を誘発する。
結論として、統合失調症患者由来の抗NCAM1自己抗体はマウスの統合失調症関連行動を引き起こし、シナプスを変化させる。抗NCAM1自己抗体は、潜在的な治療ターゲットであると同時に、異種性のある統合失調症患者集団において、小さいながらも治療可能なサブグループを区別するバイオマーカーとして機能する可能性がある。
Keywords: schizophrenia, NCAM1, anti-NCAM1 autoantibody, immunopsychiatry
論文紹介:Y.S. (医学類4年)
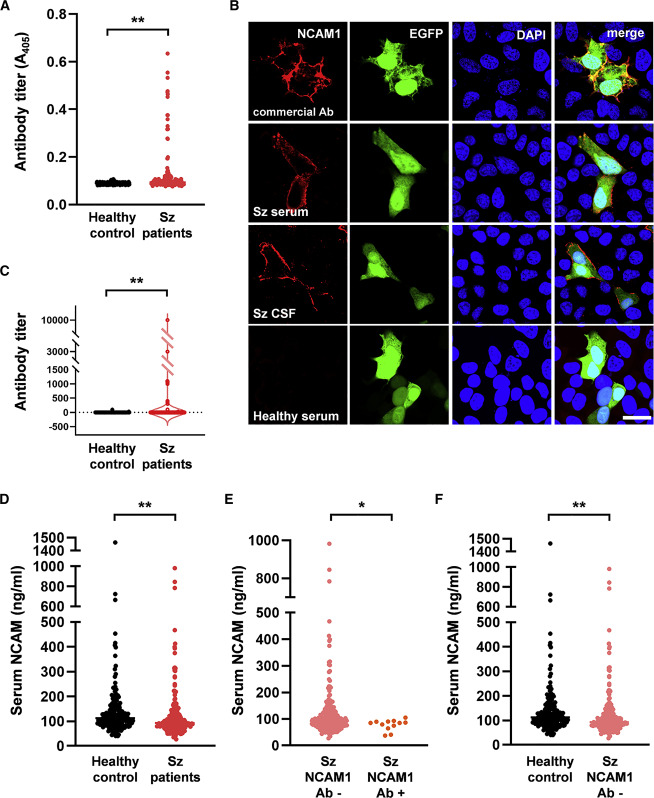
(A) Titers of anti-NCAM1 autoantibodies in serum by ELISA. ∗∗p < 0.01 (n = 201, healthy controls; n = 223, patients with schizophrenia; Mann-Whitney U test).
(B) Immunocytochemistry using a commercial anti-NCAM1 antibody, serum and CSF from schizophrenia patient 1, and serum from healthy controls. NCAM1 and EGFP were expressed from a plasmid. Confocal images show antibodies bound to the membrane of EGFP-positive HeLa cells. Similar results were obtained for all anti-NCAM1 antibody-positive patients with schizophrenia (Figure S1B). Antibodies in serum did not react with EGFP because (1) they did not react with EGFP in the nucleus and (2) they did not react with cells transfected with an empty plasmid expressing only EGFP (data not shown). Scale bar: 10 μm. Ab, antibody; Sz, schizophrenia.
(C) Titers of anti-NCAM1 autoantibodies in serum by cell-based assay. ∗∗p < 0.01 (n = 201, healthy controls; n = 223, patients with schizophrenia; Mann-Whitney U test).
(D) ELISA analysis of serum-soluble NCAM in healthy controls (n = 201) and patients with schizophrenia (n = 223). ∗∗p < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney U test).
(E) ELISA analysis of serum-soluble NCAM in schizophrenia patients with (n = 211) or without (n = 12) anti-NCAM1 autoantibodies defined by cell-based assay. ∗p < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test).
(F) ELISA analysis of serum-soluble NCAM in healthy controls (n = 201) and schizophrenia patients without anti-NCAM1 autoantibodies (n = 211) defined by cell-based assay. ∗∗p < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney U test).
「 統合失調症でシナプスを障害する自己抗体を発見 」【髙橋英彦 教授、塩飽裕紀 助教】
統合失調症患者の一部にシナプスを障害する自己抗体が存在することを発見-東京医歯大

