Neuroscience Bulletin volume 38, pages841–856 (2022) Original Article
Published: 09 June 2022
KIF17 Modulates Epileptic Seizures and Membrane Expression of the NMDA Receptor Subunit NR2B (KIF17はてんかん発作とNMDA受容体サブユニットNR2Bの細胞膜発現を調節する)
Yan Liu, Xin Tian, Pingyang Ke, Juan Gu, Yuanlin Ma, Yi Guo, Xin Xu, Yuanyuan Chen, Min Yang, Xuefeng Wang & Fei Xiao
Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing Key Laboratory of Neurology, Chongqing, 400016, China (重慶医科大学附属第一医院)
Abstract
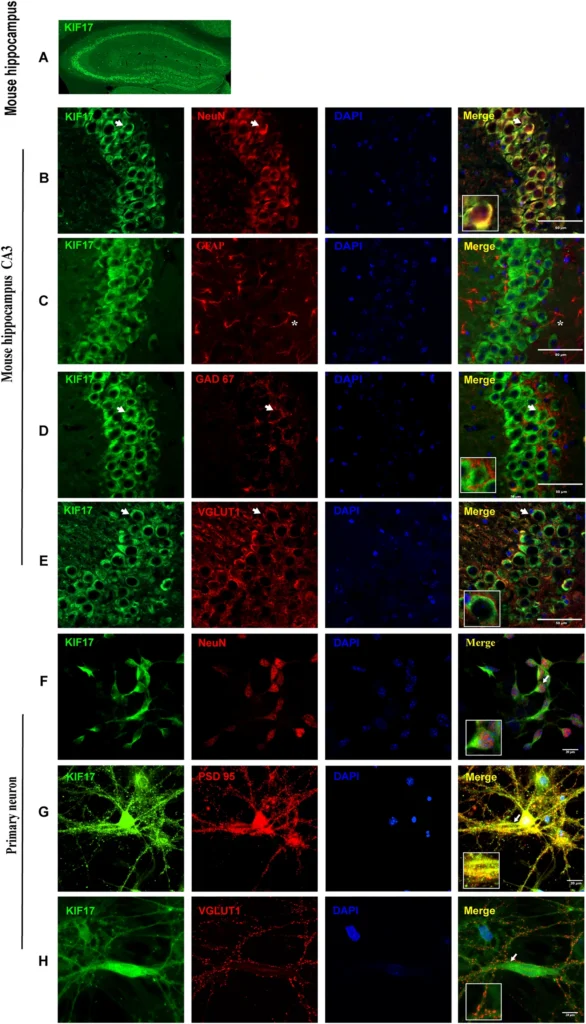
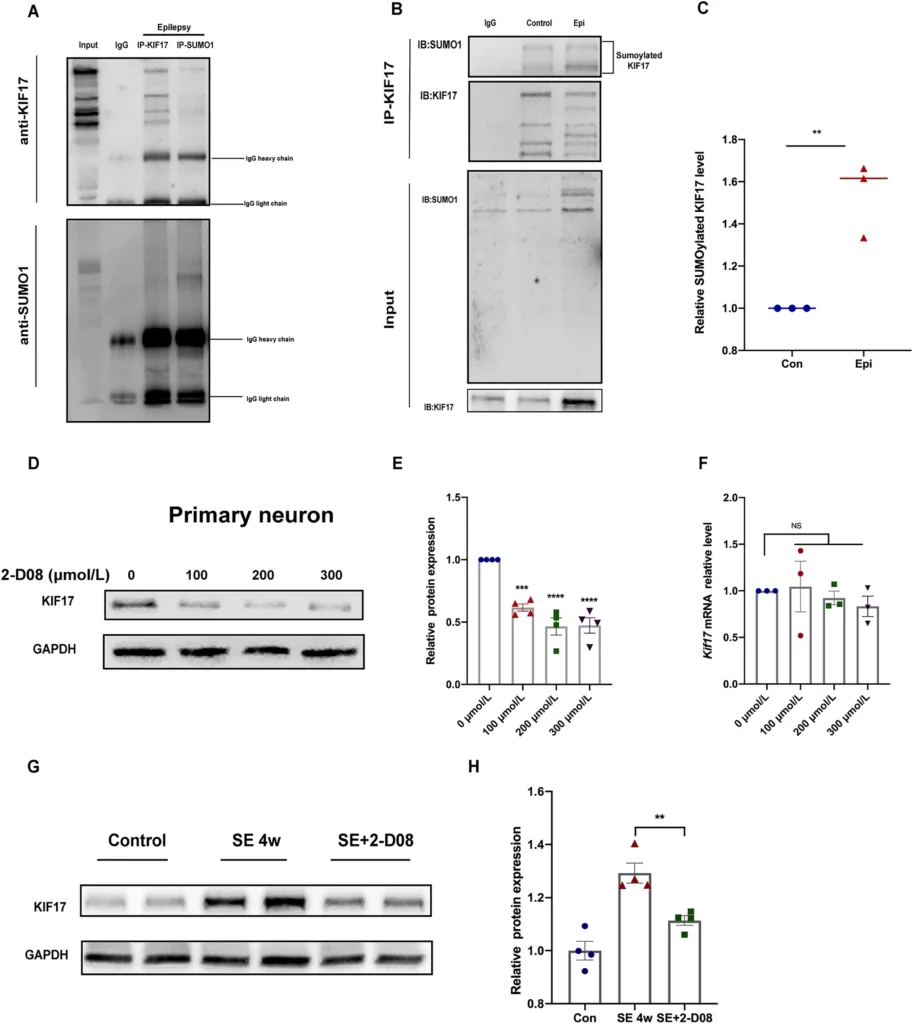
Epilepsy is a common and severe brain disease affecting >65 million people worldwide. Recent studies have shown that kinesin superfamily motor protein 17 (KIF17) is expressed in neurons and is involved in regulating the dendrite-targeted transport of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B (NR2B). However, the effect of KIF17 on epileptic seizures remains to be explored. We found that KIF17 was mainly expressed in neurons and that its expression was increased in epileptic brain tissue. In the kainic acid (KA)-induced epilepsy mouse model, KIF17 overexpression increased the severity of epileptic activity, whereas KIF17 knockdown had the opposite effect. In electrophysiological tests, KIF17 regulated excitatory synaptic transmission, potentially due to KIF17-mediated NR2B membrane expression. In addition, this report provides the first demonstration that KIF17 is modified by SUMOylation (SUMO, small ubiquitin-like modifier), which plays a vital role in the stabilization and maintenance of KIF17 in epilepsy.
概要
てんかんは、世界中で6,500万人以上が罹患している一般的かつ重篤な脳疾患である。最近の研究では、キネシンスーパーファミリーのモータータンパク質17(KIF17)が神経細胞に発現し、N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B(NR2B)の樹状突起の輸送制御に関与していることが示されている。しかし、てんかん発作に対するKIF17の効果については、まだ検討されていない。我々は、KIF17が主に神経細胞に発現していること、てんかん脳組織でその発現が増加していることを明らかにした。カイニン酸(KA)誘発てんかんモデルマウスにおいて、KIF17の過剰発現はてんかん発作の重症度を増加させたが、KIF17のノックダウンでは逆の効果がみられた。電気生理学的試験において、KIF17は興奮性シナプス伝達を制御しており、これはKIF17を介したNR2B膜の発現に起因する可能性があることがわかった。さらに、本報告では、KIF17がSUMO化(SUMO, small ubiquitin-like modifier)によって修飾されていることを初めて示し、てんかんにおけるKIF17の安定化と維持に重要な役割を果たすことを明らかにした。
医学群医学類のSさんが上記の論文を紹介しました。次に研究生のWさんがプログレスセミナーを行いました。
